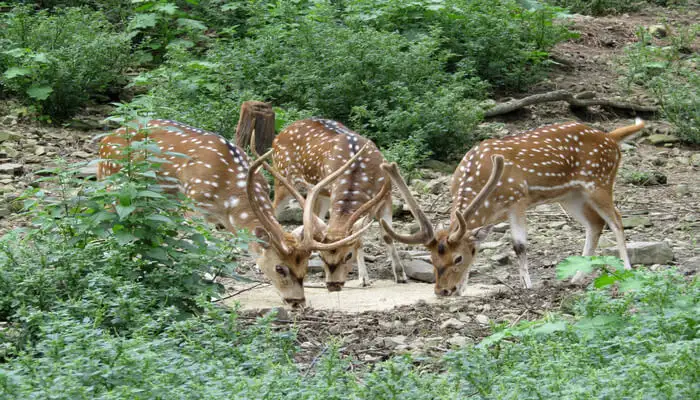
Conserving Biodiversity : Exploring Himachal Wildlife Sanctuaries and National Parks
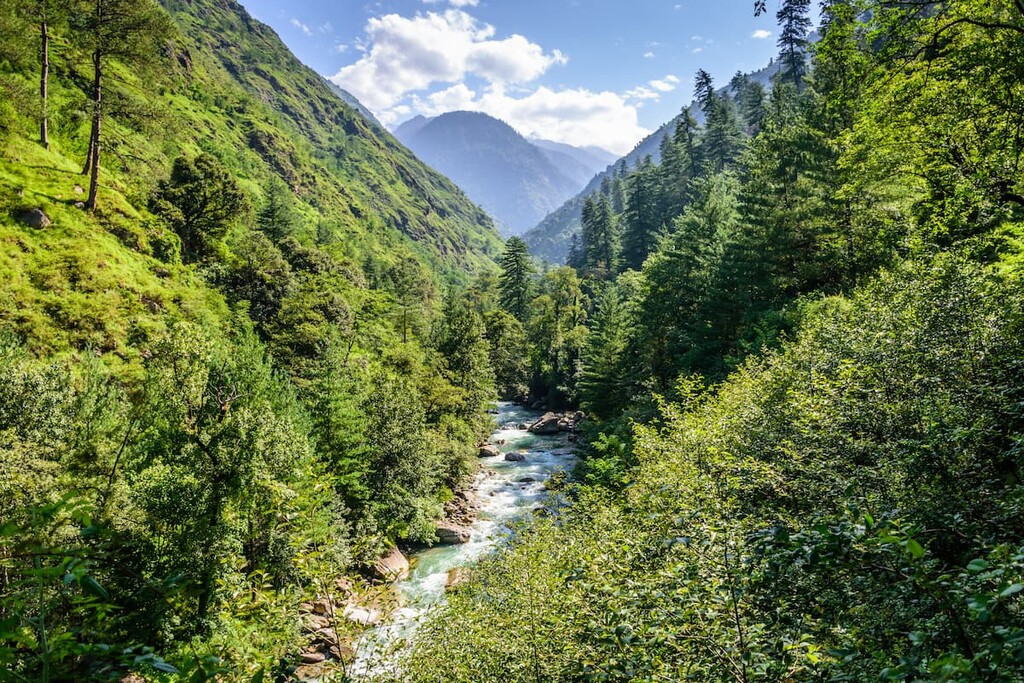
Himachal Pradesh, nestled in the lap of the Himalayas, is not only renowned for its breathtaking landscapes but also its rich biodiversity. The state is home to several wildlife sanctuaries and national parks, each playing a crucial role in the conservation of diverse flora and fauna. In this article, we delve into the vibrant world of Himachal Wildlife Sanctuaries and National Parks , showcasing the efforts made to preserve its unique ecological treasures.


1. The Great Himalayan National Park (GHNP): A UNESCO World Heritage Site
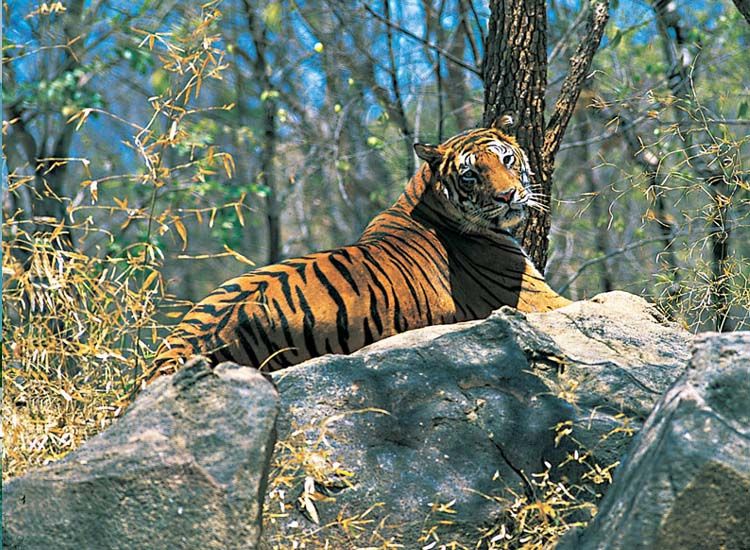
One of Himachal’s crowning jewels is the Great Himalayan National Park, designated as a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Spread across the Kullu region, the park is a haven for a variety of wildlife, including the elusive snow leopard, Himalayan brown bear, and the colorful Western Tragopan. GHNP is not only a biodiversity hotspot but also a center for research and conservation initiatives.
2. Pin Valley National Park: High Altitude Ecosystems
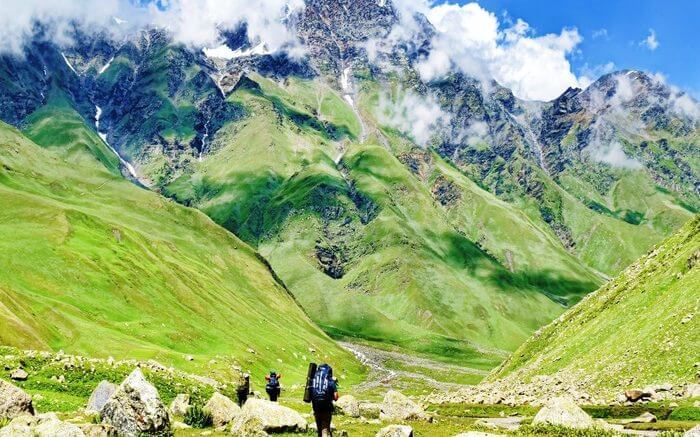
Located in the cold desert region of Spiti, Pin Valley National Park stands as a testament to the resilience of life in high-altitude ecosystems. The park is home to endangered species such as the snow leopard, Siberian ibex, and Himalayan snow cock. The unique landscape and flora of Pin Valley contribute to its significance in the conservation map of Himachal Pradesh.
3. Simbalbara Wildlife Sanctuary: A Riverside Sanctuary
Situated along the banks of the Yamuna River, Simbalbara Wildlife Sanctuary is known for its lush greenery and diverse avian population. The sanctuary provides a haven for various species of pheasants, along with mammals like the Himalayan black bear and barking deer. Simbalbara’s riparian ecosystem is vital for both resident and migratory bird species.
4. Kalatop Khajjiar Sanctuary: A Biodiversity Hotspot
Encompassing the picturesque landscapes of Dalhousie, the Kalatop Khajjiar Sanctuary is a biodiversity hotspot in Himachal. From dense deodar forests to grassy meadows, the sanctuary is home to a variety of fauna, including the Himalayan black marten, leopard, and several species of pheasants.
Also read – https://himachal.blog/solang-valley-tourism/
5. Chail Wildlife Sanctuary: Royal Retreat for Wildlife
Once the private hunting ground of the Maharaja of Patiala, Chail Wildlife Sanctuary is now a refuge for various species, including the cheer pheasant and the Himalayan goral. The sanctuary’s mixed deciduous forests and grasslands contribute to the overall conservation of wildlife in the region.
Conservation Initiatives and Challenges:
While these sanctuaries and national parks play a crucial role in preserving Himachal’s biodiversity, challenges such as habitat fragmentation, human-wildlife conflict, and climate change persist. Various initiatives have been implemented to conserve Himachal Wildlife Sanctuaries and National Parks, recognizing the importance of preserving its rich biodiversity. Some notable initiatives include:
Conclusion:
Himachal Pradesh’s commitment to conserving its biodiversity through wildlife sanctuaries and national parks reflects a harmonious coexistence between human activities and nature. As visitors traverse these protected areas, they not only witness the awe-inspiring beauty of the Himalayan ecosystems but also actively contribute to the ongoing efforts to safeguard these natural treasures for generations to come. The delicate dance between conservation and exploration ensures that Himachal Wildlife Sanctuaries and National Parks continue to thrive against the backdrop of its majestic landscapes.