Apple Farming and Other Essential Things you Must Know
The apple fruit is the most popular and profitable temperate fruit to be produced commercially. In addition, the apple is the fourth-most widely cultivated organic fruit worldwide, after oranges, bananas, and grapes. The world's largest apple producer is China. It is primarily grown in Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and the foothills of Uttar Pradesh in India. However, the apple industry also expanded to Nagaland, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, and Meghalaya.


Apples are primarily consumed fresh, although a small portion of the harvest is used to make jams, juices, canned slices, and confections.
Factors Usually Required for Apple Farming
Apple farming is possible between 1,500 and 2,700 meters above sea level in the Himalayan region. It endures 1,000 to 1,500 hours of chilling or cooling per year.
The ideal temperature range for the apple growth season is between 21 and 24 °C. For optimal growth and production, apple trees require between 100 and 125 cm of regular annual precipitation.
It would also lead to poor fruit quality, improper color, and expansion of fungal development on the fruit surface if there was excessive precipitation near the fruit vegetative phase.
In areas where significant wind speeds are predicted, there are other options than apple cultivation procedures.
Soil Specifications for Apple Farming
Apple farming techniques work best on loamy soils rich in organic matter with pH levels between 5.5 and 6.5. To ensure effective apple growth techniques, the soil used for growing apples must stay waterlogged.
Apple farming requires soil with sufficient drainage and should be clean. Apples grow well in deep loam soil. However, you can also use well-drained clay-loam soils.
Apple trees are negatively impacted in sandy-loam soils by insects, including stem and root borers, and stem diseases like canker and papery bark. However, the gravelly, shallow soils can be rendered appropriate by adding significant amounts of farmyard manure, compost, or leaf mold.
Apple farming works best on soils high in organic matter, have a pH of about 6.5, and have proper drainage.
Apple Farming Techniques for Planting
Two weeks before planting, 60 cm diameter pits are dug. First, good loamy soil and organic matter are buried in the pits. Then, scooping up some soil, you place the soil ball in the center of the pit, preserving the roots.
The remaining space is filled with loose dirt and lightly pressed to seal air spaces. The seedlings are immediately staked and watered. As a result, on average, 80 to 500 plants can be found in an acre of space.
There are four main planting density classifications: low density (less than 120 apple plants per acre). Moderate density (between 120 and 200 apple plants per acre). High density (between 200 and 520 plants per acre) and ultra-high density (more than 520 plants per acre).
Apple plant spacing and planting density per unit area is based on the combination of stem and rootstock varieties.
For good apple fruit production, pollinator species must be cultivated between the primary species. For example, the Horticulture Department advises planting Red Delicious and Golden Delicious as pollinators for establishing Royal Delicious varieties.
The contour approach is typically used on slopes, whereas hexagonal or square estate arrangements are used in valleys. To produce high-quality apples for apple farming, a pollinator ranch of parent species is created in the middle of the parent species.
In October and November, burrow pits with dimensions of 1 m x 1 m x 1 m are prepared for planting. After correctly blending, 50 grams of Malathion dust, 500 grams of Single superphosphate, and 30 to 40 kg of Farm Yard Manure (FYM) are added to each pit.
After thoroughly mixing, 30 to 40 kg of Farm Yard Manure (FYM), 500 grams of Single Superphosphate, and 50 grams of Malathion dust are added to each pit. Apple growing is immediately followed by one irrigation.
You may also read- https://himachal.blog/a-brief-on-agriculture-and-farming-subsidies-in-india/
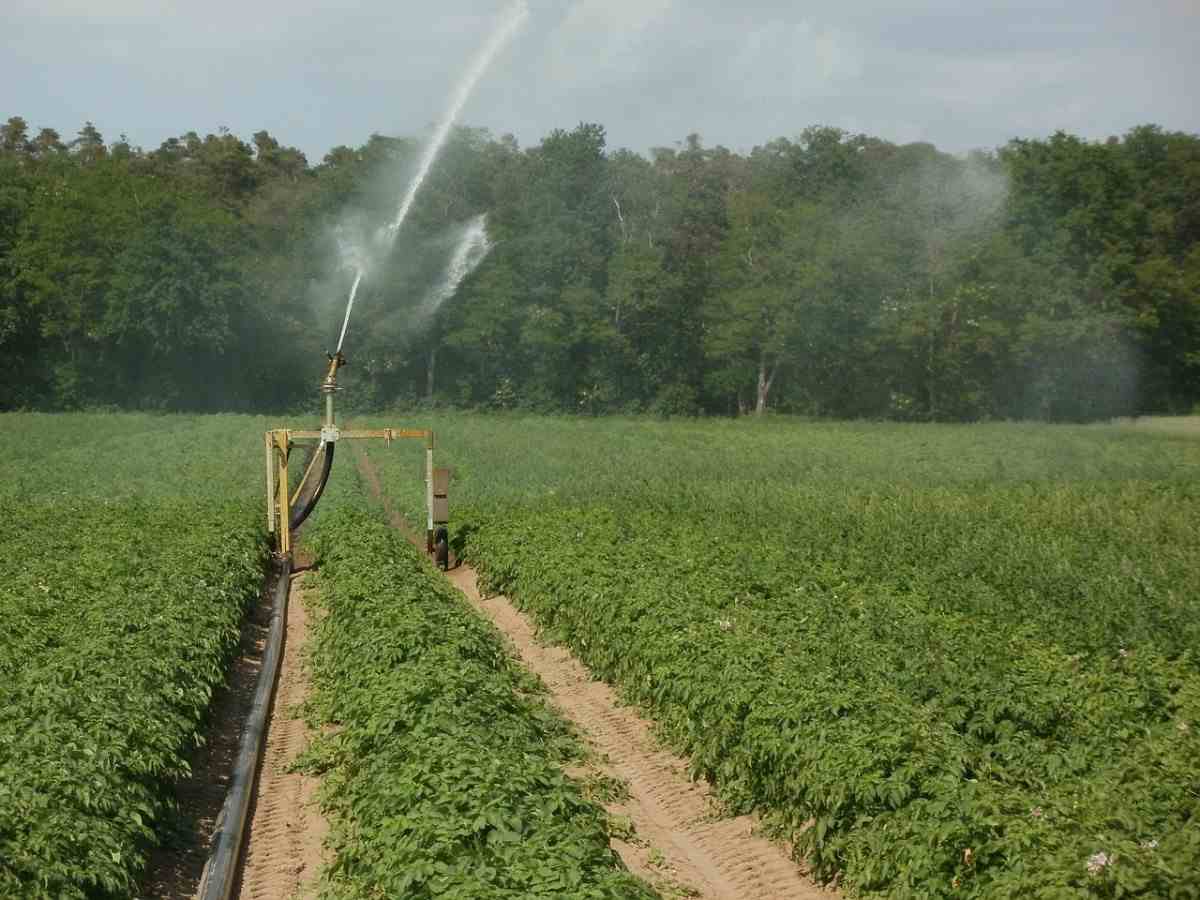
Irrigation
Low soil moisture can be particularly damaging to apple trees. The number and size of fruits are decreased, and the June drop is increased when there is water stress during the growing season. In the event of dry spells during the key moment, supplemental irrigation should be offered. The viability of the apple crop largely depends on the even distribution of rain throughout the year.
Poor seed yield, excessive fruit drop, low output, and poor quality are all effects of water deficit.
The months of April through August have the highest water demand. Apple farming requires about 115 cm of water per year, which should be scheduled for 14 to 20 irrigations.
In the summer, watering should be sprayed every six to ten days, while in the winter, it should be sprayed every month or so.
At least eight irrigations are anticipated during the key season, which runs from April to August.
2 comments
Leave a comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.














Your blog is an excellent source for details on related topics.
Great Article
http://www.apneehatti.com