Chikungunya: Beating the Bite
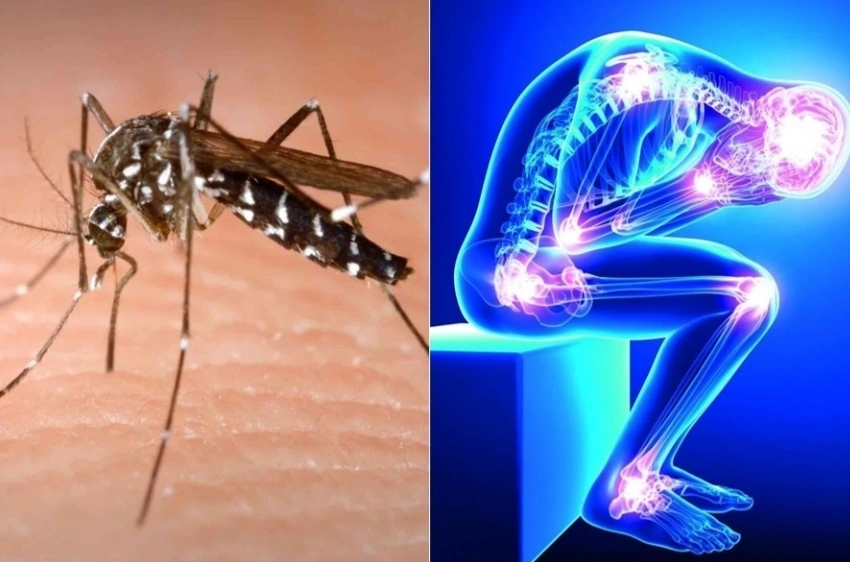
Chikungunya is a viral infection caused by the chikungunya virus (CHIKV), tha's primarily transmitted to humans through the bites of infected mosquitoes. The name "chikungunya" comes from the Kimakonde language, meaning "to walk bent over," referring to the characteristic posture of those suffering from joint pain.


Cause of chikungunya:
Mosquito Bites: Immediate mode of transmission is through the bite of infected mosquitoes. When a female Aedes mosquito bites a person infected with chikungunya, it takes up the virus along with the blood meal. The virus then replicates in the mosquito’s body, eventually reaching the salivary glands. Subsequently, when the infected mosquito bites another person, it can transmit the virus through its saliva into the person’s bloodstream, leading to infection.
How it spreads:
- Travel and Migration: Chikungunya can spread to new regions when infected individuals travel from areas with active transmission to areas where the virus is not commonly found. This can potentially trigger outbreaks in previously unaffected regions.
- Mother-to-Child Transmission: While rare, there have been reported cases of chikungunya transmission from an infected pregnant mother to her child during childbirth or through breastfeeding.
- Blood Transfusions and Organ Transplants: In very rare cases, chikungunya can also be transmitted through blood transfusions and organ transplants from infected donors.
You may also read – https://himachal.blog/hi/chickenpox-symptoms-and-prevention/
Symptoms of Chikungunia:
Sudden High Fever: Chikungunya is characterized by a sudden onset of high fever, often reaching 102°F (38.9°C) or higher. The fever can be accompanied by chills.
Severe Joint Pain: The joint pain associated with Chikungunya is usually symmetrical and can be very intense. It commonly affects the joints of the hands, wrists, ankles, and feet. The pain can make movement difficult and may last for weeks or even months in some cases.
Muscle Pain: Muscle aches and pain, known as myalgia, are common symptoms of the infection.
Headache: Many people with Chikungunya experience headaches, which can range from mild to severe.
Fatigue: Fatigue and weakness are often reported during the acute phase of the illness.
Skin Rash: Some individuals may develop a rash that can be itchy. The rash is usually maculopapular (red spots with raised bumps) and may appear on the trunk and limbs.
Nausea and Vomiting: Gastrointestinal symptoms like nausea and vomiting can occur in some cases.
There is no specific vaccine or cure for chikungunya, prevention is crucial in controlling the spread of the virus.Prevention plays a crucial role in controlling the spread of the virus and reducing the risk of this infection.
How to prevent:
- Apply mosquito repellents containing DEET, picaridin, etc to exposed skin and clothing. Carefully read and follow the instructions the on the product label.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, socks, and shoes to reduce exposed skin.
- Use bed nets while sleeping, especially if you are in an area where mosquito-borne diseases like chikungunya are prevalent.
- Keep windows and doors closed and Repair tears in window or door screens to keep mosquitoes and other insects from entering your living spaces.
- Mosquitoes breed in stagnant water. Regularly empty, clean, or cover containers that can hold water, such as flower pots, buckets, old tires, and pet water bowls.
- Avoid traveling to areas reported with chikungunya.
Keep Emptying water from containers, like under potted plants, vases, buckets, and rain gutters.
Diagnosis of Chikungunya
IgM Antibody Test: A positive IgM test indicates a recent or current Chikungunya infection.
IgG Antibody Test: A positive IgG test suggests a past Chikungunya infection or immunity due to previous exposure.
Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR): This test detects the viral RNA in the blood during the acute phase of the infection (usually within the first week of symptoms).
It’s essential to note that cross-reactivity can occur with other viruses like dengue, so further testing and interpretation may be necessary to differentiate between these infections.
Conclusion
Chikungunya is not a deadly infection, and the majority of people who become infected will recover on their own without any specific treatment. However, the symptoms can be quite uncomfortable and can persist for weeks or even months in some cases. So it’s essential to see a doctor as soon as the first symptoms appear.
Buying Mosquito traps, along with other preventive measures, can be helpful in minimizing mosquito bites and lowering the risk of acquiring Chikungunya or other mosquito-borne illnesses and do follow all the suggestions in this blog to protect yourself from Chikungunya.